Studies on Structures and
Dynamic Properties of Peroxide-Crosslinked EPDMs, Part 3
Changes in Molecular Mobility and Crosslinking Density Caused by Carbon
Black
Hitoshi Iwabuki
Industrial Technology Center of Okayama Prefecture, Okayama,Japan
Kazuya Nagata
Industrial Technology Center of Okayama Prefecture, Okayama,Japan
Toru Noguchi
Nissin Kogyo Co., Ltd, Nagano,Japan
Eisuke Yamada
Aichi Institute of Technology, Aichi,Japan
Nippon Gomu Kyokaishi,(2003),76(12), 429-435
Original Paper in Japanese.
Abstract
Peroxide-crosslinked
EPDMs filled with various kinds of carbon black (CB) were examined by
 pulsed
NMR. The signal of spin-spin relaxation time (T2)
measured by Hahn echo method was resolved into two components, T2n
and T2nn, which correspond to the network molecules
and the non-network molecules respectively. For the non-crosslinked EPDMs
filled with CB, T2n and T2nn
became shorter with the increase in the specific surface area of CB, though
the degree of the decrease in the molecular mobility was smaller in the
case of the network component. For the crosslinked EPDMs, T2n
and T2nn became longer with the increase in the
specific surface area of CB, suggesting that the presence of the CB obstructs
the crosslinking. The crosslinking density of rubber phase ( pulsed
NMR. The signal of spin-spin relaxation time (T2)
measured by Hahn echo method was resolved into two components, T2n
and T2nn, which correspond to the network molecules
and the non-network molecules respectively. For the non-crosslinked EPDMs
filled with CB, T2n and T2nn
became shorter with the increase in the specific surface area of CB, though
the degree of the decrease in the molecular mobility was smaller in the
case of the network component. For the crosslinked EPDMs, T2n
and T2nn became longer with the increase in the
specific surface area of CB, suggesting that the presence of the CB obstructs
the crosslinking. The crosslinking density of rubber phase (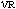 )
were calculated from the relationship between the apparent crosslinking
density ( )
were calculated from the relationship between the apparent crosslinking
density (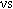 )
and the reciprocal of T2n (1/T2n)
for unfilled EPDMs. The crosslinking density related to CB ( )
and the reciprocal of T2n (1/T2n)
for unfilled EPDMs. The crosslinking density related to CB (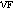 )
were obtained from the difference between )
were obtained from the difference between 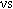 and
and 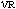 for CB-filled EPDMs. The
for CB-filled EPDMs. The 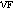 values showed good correlation with the tensile stress at 100% elongation.
values showed good correlation with the tensile stress at 100% elongation.
Keywords:
EPDM, Peroxide, Carbon black, Pulsed NMR, Hahn echo method, Molecular
mobility, Crosslinking density |